Our eosinophilosophy
eos counts in
HYPEREOSINOPHILIC SYNDROME
Hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) is a rare group of disorders characterized by peripheral hypereosinophilia with eosinophil-mediated organ dysfunction and/or damage, with no other identifiable etiology for eosinophil-mediated organ damage.1,2 US estimated prevalence of HES is 5000 patients.3,4
Known mechanisms of hypereosinophilia5
The exact mechanism of hypereosinophilia for other subtypes of HES is not well established.
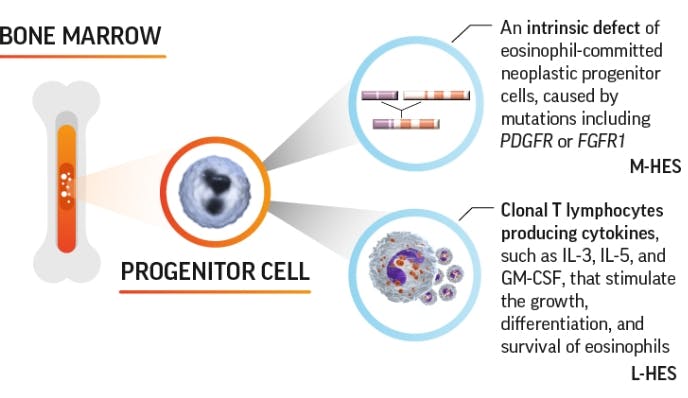
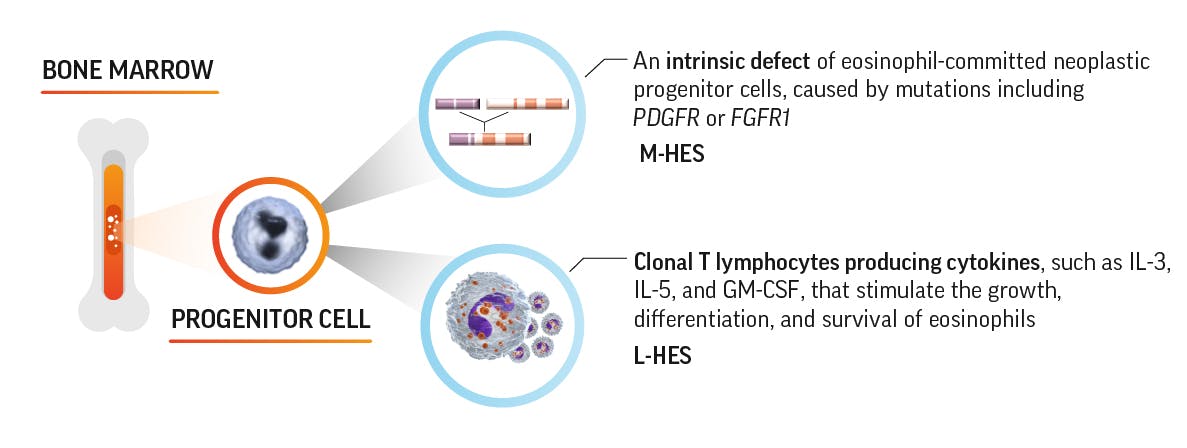
FGFR1=fibroblast growth factor receptor 1; GM-CSF=granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IL=interleukin;
L-HES=lymphocytic variant HES; M-HES=myelproliferative-variant HES; PDGFR=platelet-derived growth factor receptor.

Elevated eosinophils contribute to organ damage
Clinical manifestations of HES vary depending on the organs affected by eosinophils and this can change over time.2,4
The organs that are targeted can vary, which results in differing clinical manifestations. These include2,4:
Cardiovascular
Central nervous system
Constitutional
Dermatologic
Gastrointestinal
Peripheral nervous system
Pulmonary
EOS counts in HES diagnosis and
treatment decisions

Hypereosinophilia is a defining characteristic of HES. Hypereosinophilia is defined as1:
- Blood EOS count of >1500 cells/µL on 2 occasions with an interval of 1 month or longer
- Histologically proven eosinophilia in tissue (defined by 1 or more of the following):
- Bone marrow aspiration with >20% eosinophils
- Histologically proven tissue infiltration
- Deposition of eosinophil-granule proteins
and/or
Sustained hypereosinophilia without an apparent cause
should prompt a workup and consideration of HES1
Could it be EGPA or a single-organ restricted disease?
Differentiating between HES and eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) is challenging—both conditions have persistent eosinophilia and systemic manifestations.6
EGPA characteristics that differ from HES include6-8:
- Asthma and nasal polyps
- Vasculitic complications
- Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-positivity (in ~40% of patients)
Differentiating between HES and single organ-restricted disease can be challenging. The magnitude of blood eosinophilia, with a combination of clinical and laboratory results, and pathologic and radiographic findings may be useful for differentiating HES from single-organ disease including (but not limited to)1,9:
Eosinophil counts can help guide treatment decisions
Per the World Health Organization’s 2019 update on eosinophilic disorders, the goal of therapy in patients with hypereosinophilia is to mitigate eosinophil-mediated organ damage.10
References:
- Valent P, Klion AD, Horny HP, et al. Contemporary consensus proposal on criteria and classification of eosinophilic disorders and related syndromes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130(3):607-612.e9.
- Ogbogu PU, Bochner BS, Butterfield JH, et al. Hypereosinophilic syndrome: a multicenter, retrospective analysis of clinical characteristics and response to therapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;124(6):1319-25.e3.
- Wilkins HJ, Crane MM, Copeland K, Williams WV. Hypereosinophilic syndrome: an update. Am J Hematol. 2005;80(2):148-157.
- Roufosse FE, Goldman M, Cogan E. Hypereosinophilic syndromes. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007;2:37.
- Leru PM. Eosinophilic disorders: evaluation of current classification and diagnostic criteria, proposal of a practical diagnostic algorithm. Clin Transl Allergy. 2019;9:36.
- Leurs A, Chenivesse C, Lopez B, et al. C-Reactive protein as a diagnostic tool in differential diagnosis of hypereosinophilic syndrome and antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-negative eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2019;7(4):1347-1351.
- Vaglio A, Buzio C, Zwerina J. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss): state of the art. Allergy. 2013;68(3):261-273.
- Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Bacon A, et al. 2012 Revised international Chapel Hill consensus conference nomenclature of vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(1):1-11.
- Wechsler ME. Pulmonary eosinophilic syndromes. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2007;27(3):477-492.
- Shomali W, Gotlib J. World Health Organization-defined eosinophilic disorders: 2019 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and management. Am J Hematol. 2019;94(10):1149-1167.
